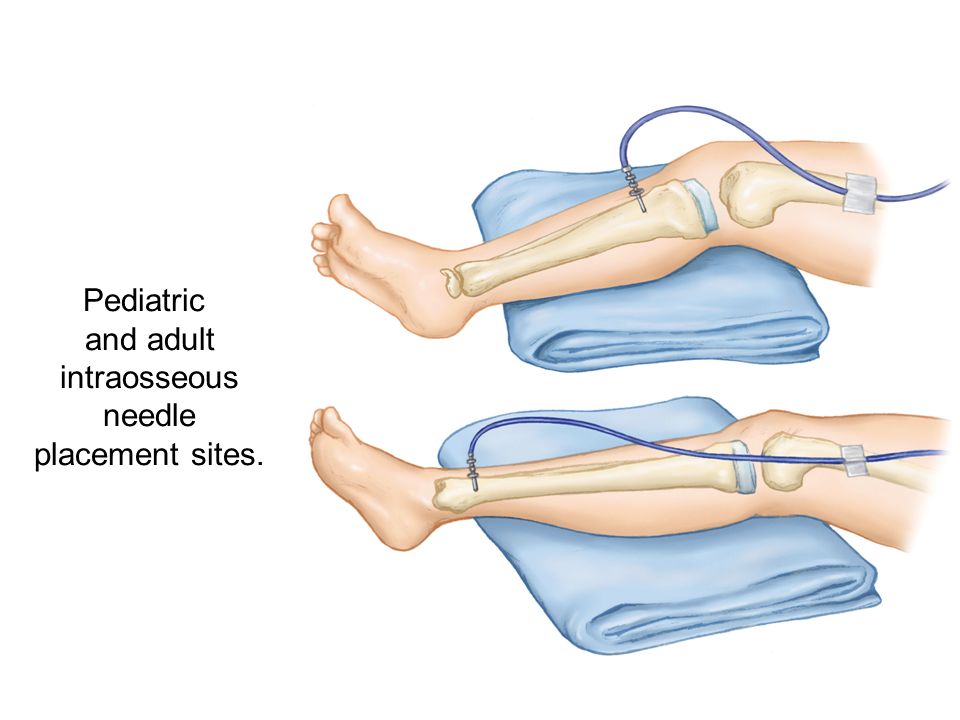
Intraosseous Drug Administration. 6 via the intraosseous route. Intraosseous versus intravenous drug administration in patients with out of hospital cardiac arrest to compare the effectiveness of the intravenous iv and intraosseous io routes for drug administration in adults with a cardiac arrest enrolled in the pre hospital assessment of the role of adrenaline nolan et al 2020. This provides a non collapsible entry point into the systemic venous system. Io access uses the highly vascularized bone marrow to deliver fluids and medications during cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
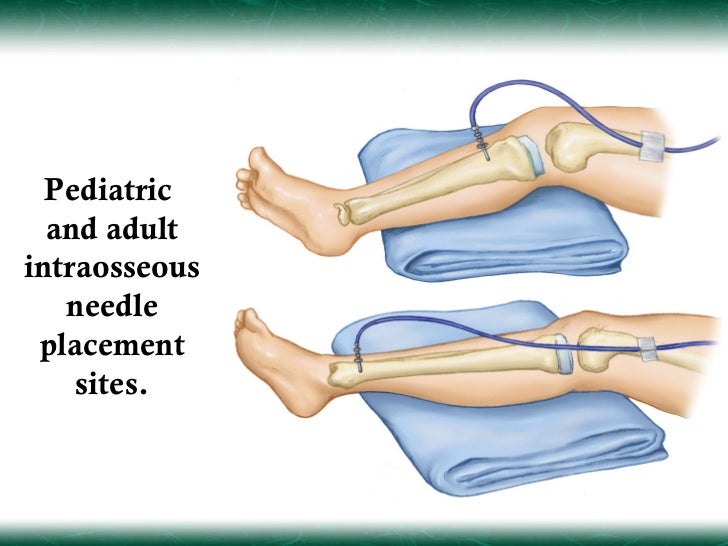
Marrow cannot always be aspirated but it should flush easily. In the neonate intraosseous access may be easier and quicker than umbilical vein catheterisation in an emergency. To administer a medication via the io route. Io access uses the highly vascularized bone marrow to deliver fluids and medications during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Intraosseous infusion is the process of injecting directly into the marrow of a bone. Secure the needle and start the infusion this needs to be manually administered as boluses with the 20 ml syringe.
This provides a non collapsible entry point into the systemic venous system.
The patient s history and perform a physical obtain examination. Death during event within 24 hours and before hospital discharge. Intraosseous versus intravenous drug administration in patients with out of hospital cardiac arrest to compare the effectiveness of the intravenous iv and intraosseous io routes for drug administration in adults with a cardiac arrest enrolled in the pre hospital assessment of the role of adrenaline nolan et al 2020. Indeed intraosseous infusion is now preferred over the endotracheal route to administer drugs during advanced life support in adults the endotracheal route being no longer used. This technique is used to provide fluids and medication when intravenous access is not available or not feasible. This provides a non collapsible entry point into the systemic venous system.