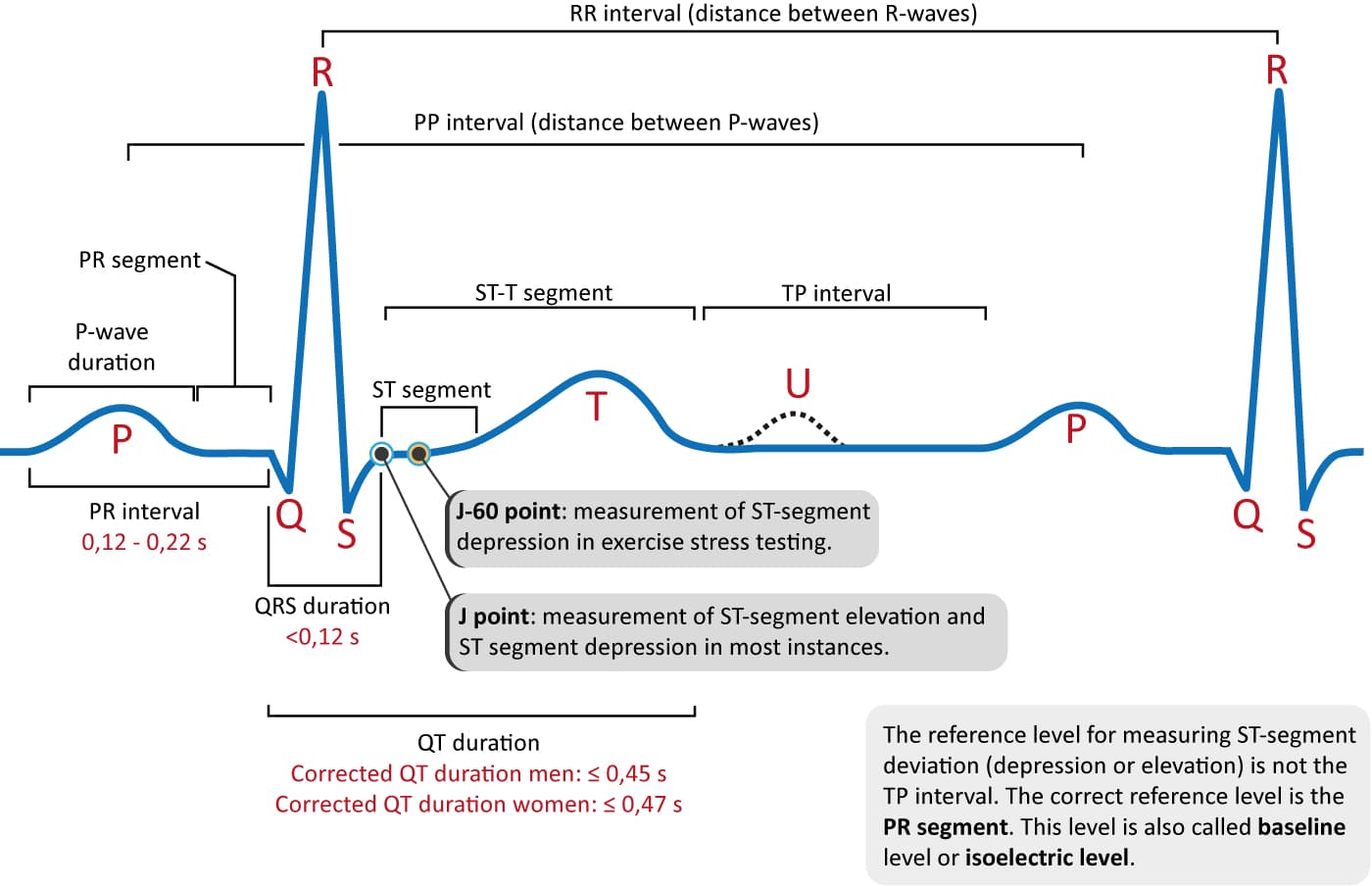
Ecg Graph Interpretation. Av nodal conduction resumes with the next beat and the sequence of progressive pr interval prolongation and the eventual dropping of a qrs complex repeats itself. Analysis and interpretation of the electrocardiogram. The horizontal axis measures the time and rate while the vertical axis measures the amplitude or voltage. An ekg is a representation of the electrical activity of the heart muscle as it changes with time usually printed on paper for easier analysis.
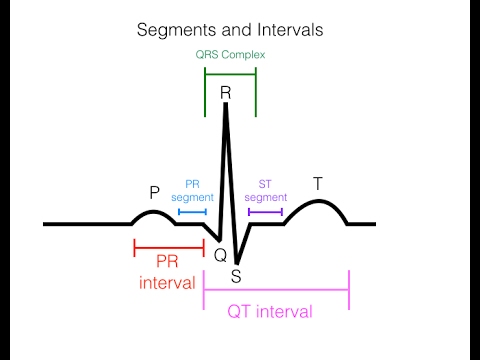
Electrocardiogram ecg ekg is a tool used to visualize the electricity that flows through the heart. When looking at an ecg you ll notice that it is shown on a graph. A wave facing upwards is called a positive deflection and a wave facing downwards is called a negative deflection. It is used to check for the rhythm of your heart that could indicate whether it is normal or abnormal. Typical ecg findings in mobitz type 1 av block include progressive prolongation of the pr interval until eventually the atrial impulse is not conducted and the qrs complex is dropped. The 12 lead ecg.
When you visit the doctor for ecg they will place 10 to 12 electrodes all over your chest and record the electrical activity of the heart.
An ecg electrode is a conductive pad which is attached to the skin to record electrical activity. Analysis and interpretation of the electrocardiogram. When looking at an ecg you ll notice that it is shown on a graph. The ecg must always be interpreted systematically. A 12 lead ecg records 12 leads producing 12 separate graphs on a piece of ecg paper. This electrical activity is recorded on the ecg machine and is represented as a graph.