
Define Deontological Theory. This ethical theory is most closely associated with german philosopher immanuel kant. Actions that obey these rules are ethical while actions that do not are not. Kant believed that ethical actions follow universal moral laws such as don t lie. Deontology is a theory that suggests actions are good or bad according to a clear set of rules.
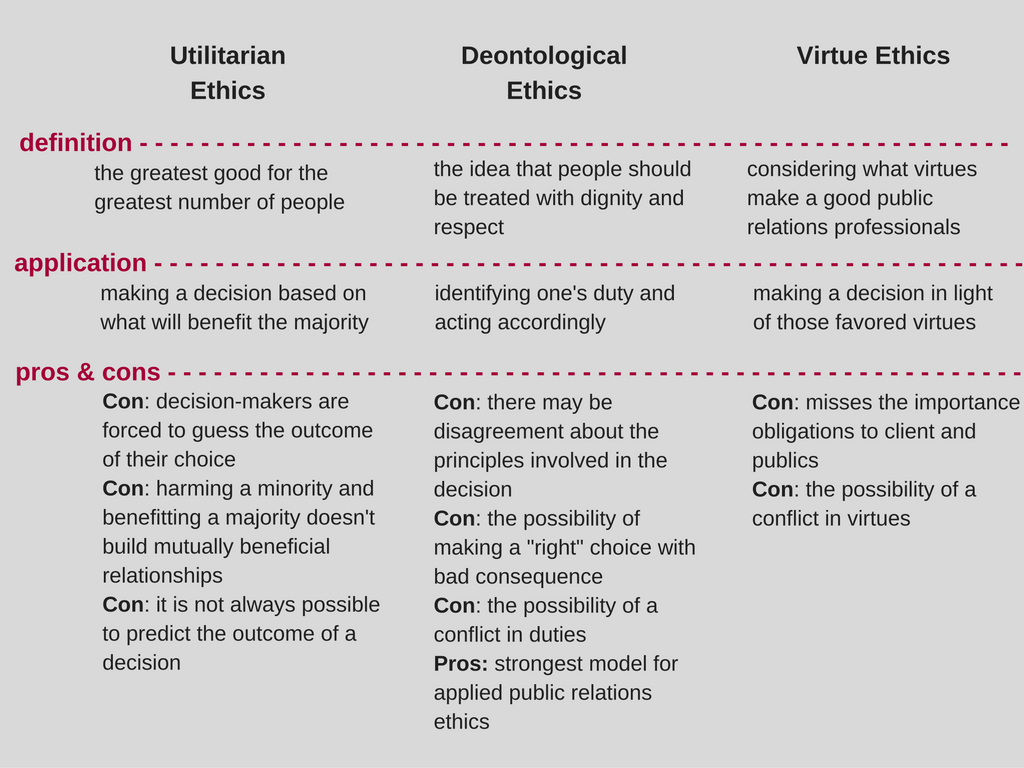
Kant s deontology is guided by an individual s own personal sense of morality or what is right and what is wrong to us. Kant was a scientist and scholar whose books included works about science. Deontology is an ethical theory that uses rules to distinguish right from wrong. The term deontology is derived from the greek deon duty and logos science. Its name comes from the greek word deon meaning duty. δέον obligation duty λόγος study is the normative ethical theory that the morality of an action should be based on whether that action itself is right or wrong under a series of rules rather than based on the consequences of the action.
It is sometimes described as duty obligation or rule based ethics.
The term deontology is derived from the greek deon duty and logos science. Deontological ethics noun used with a singular verb the branch of ethics dealing with right action and the nature of duty without regard to the goodness or value of motives or the desirability of the ends of any act. Deontology is often associated with philosopher immanuel kant. Kant believed that ethical actions follow universal moral laws such as don t lie. Deontological theory a type of ethical theory that maintains that some features of actions other than or in addition to consequences make the actions right or wrong. It is sometimes described as duty obligation or rule based ethics.